Trochanteric bursa injections: targeted relief for hip pain
Trochanteric bursa injections are a highly effective treatment option for managing hip pain caused by inflammation in the bursa, which is a fluid-filled sac that cushions and reduces friction between bones, tendons, and muscles around the joint. This procedure involves the injection of medication directly into the bursa to alleviate pain, reduce swelling, and improve joint mobility.

What is trochanteric bursitis?
Trochanteric bursitis is a condition characterised by pain and inflammation of the trochanteric bursa, a fluid-filled sac located over the greater trochanter (the bony prominence on the outer side of the hip). Bursae are found throughout the body, positioned between bones and tendons to minimise friction during movement.
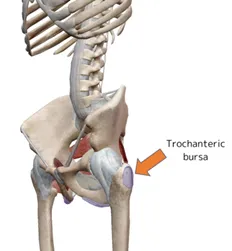
What are the causes of trochanteric bursitis?
Trochanteric bursitis can result from various factors, including:
- Sports activities, such as football and soccer, that involve extensive running and overuse of the hip joint
- Hip injuries from falls or impacts
- Bone spurs in the hip or thighbone
- Poor posture
- Leg-length discrepancies
- Complications from hip surgery
- Medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, psoriasis, or thyroid disorders
What are the symptoms of trochanteric bursitis?
Common symptoms include:
- Pain on the outer side of the hip, worsening with prolonged walking or stair climbing
- Discomfort when lying on the affected side
- Tenderness in the hip area
- Stiffness in the hip joint
- In severe cases, redness and swelling around the affected area
How is trochanteric bursitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a review of your medical history, a physical examination of the hip, and sometimes imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound.
In some cases, an anaesthetic injection may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
What is the treatment for trochanteric bursitis?
Conservative treatments are often effective and include:
- Rest, ice application, and over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g. anti-inflammatory gels)
- Physiotherapy: The key is to strengthen the core muscles around the hip joint (the hip abductor muscles).

If symptoms persist, additional treatments may be required:
- Trochanteric bursa steroid injections can help reduce inflammation and allow physiotherapy.
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy: a non-invasive treatment that uses shock waves to treat hip bursitis.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical removal of the bursa may be necessary
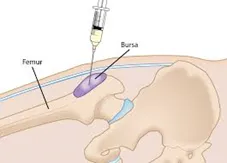
What are trochanteric bursa injections?
Trochanteric bursa injections involve injecting anti-inflammatory medication, typically corticosteroids, into the hip bursa. The bursa can become inflamed due to overuse, trauma, or underlying conditions like bursitis or arthritis, leading to significant pain and discomfort. By targeting the source of inflammation, hip bursa injections provide fast, targeted relief.
If you have persistent hip pain that limits your daily activities or if other conservative treatments have not provided adequate relief, hip bursa injections may be a suitable option. Consult with a specialist to evaluate your condition and discuss the potential benefits of this targeted pain relief method.
What are the advantages of these injections?
- Targeted pain management: Direct relief to the inflamed area.
- Quick procedure: Typically completed in a short visit.
- Minimal downtime: Most patients can return to light activities soon after.
- Non-surgical treatment: A less invasive option for managing pain.
- Long-lasting relief: Effects can last weeks to months, depending on the patient but unfortunately time duration cannot be guaranteed.
What does the procedure involve?
- Preparation: The patient is positioned comfortably, and the skin over the hip is cleaned with an antiseptic agent
- Imaging guidance: Ultrasound or fluoroscopy is sometimes used to locate the exact position of the bursa.
- Injection: A thin needle is inserted into the bursa, and the medication is administered.
- Completion: The needle is removed, and the area is cleaned and bandaged.
What is the post injection care?
- Initial recovery: Patients may experience mild discomfort at the injection site, which usually resolves within a few days.
- Activity recommendations: Light activities are encouraged, while intense physical activity should be avoided for 24-48 hours.
- Follow-up care: Monitoring for changes in pain levels and any potential side effects. Your surgeon will arrange follow-up with you and often at 6 weeks following the procedure.
What are the risks?
While hip bursa injections are generally safe, some of the potential risks include:
- Temporary pain: Mild soreness at the injection site.
- Skin reactions: Redness or slight swelling.
- Infection (rare): Proper sterile techniques minimise this risk.
- Allergic reactions: Rare but possible to medication components.
How can you prevent trochanteric bursitis?
To lower the risk of developing bursitis:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Engage in regular exercise, ensuring proper form, warm-up, and stretching
- Avoid activities that excessively strain the hips
- Use orthotic devices to correct leg-length discrepancies
- Strengthen and maintain flexibility in the hip muscles
Summary: precision pain relief for hip discomfort
Hip (trochanteric) bursa injections offer a highly effective solution for managing hip pain and inflammation. With minimal downtime and a targeted approach, these injections can help improve quality of life, allowing patients to return to their daily activities with reduced pain and enhanced joint function. Contact a specialist to see if hip bursa injections are right for you and take a step toward better hip health.
