What is knee arthroscopy?
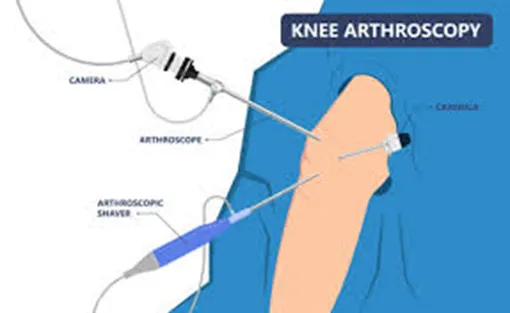
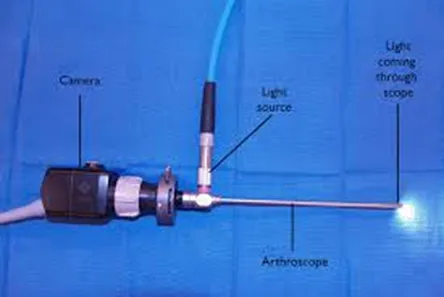
Knee arthroscopy (also known as keyhole knee surgery) is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a small camera, called an arthroscope, to view the inside of the knee joint.
This advanced technology enables surgeons to diagnose issues and perform treatments with precision through small incisions.
Using state-of-the-art tools and techniques, this procedure is designed to provide relief with minimal discomfort and downtime.
Whether you’re an athlete recovering from an injury or someone managing chronic knee pain, knee arthroscopy offers a solution tailored to your needs.
It’s commonly used for conditions such as meniscus tears, ligament injuries, and cartilage damage.
Who can benefit from knee arthroscopy?
This procedure is ideal for individuals who:
- Have persistent knee pain that doesn’t improve with non-surgical treatments.
- Experience limited range of motion or joint instability.
- Have suffered injuries like torn ligaments or cartilage.
- Need a definitive diagnosis of unexplained knee issues.
Knee arthroscopy is suitable for both active individuals and those dealing with degenerative conditions, offering a pathway to improved joint function and mobility.
What are the benefits of knee arthroscopy surgery?
- Minimally invasive with small incisions and minimal scarring.
- Reduced pain and faster recovery compared to open surgery.
- High precision in diagnosing and treating knee conditions.
- Ideal for athletes aiming for a quicker return to sports.
What are the common treatments performed during knee arthroscopy?
Knee arthroscopy can address various conditions and injuries using minimally invasive techniques.
Common treatments include:
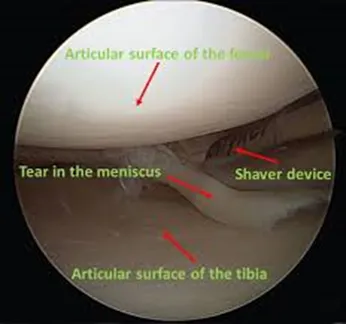
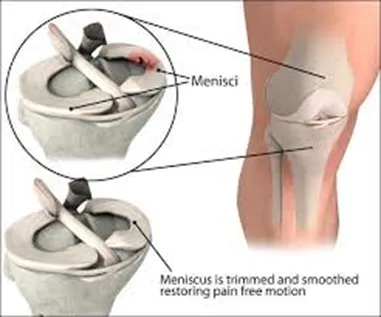
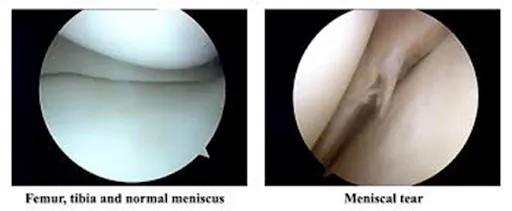
- Meniscus tears: Procedures like meniscal repair or partial meniscectomy.
- Cartilage injuries: Treatments such as microfracture or chondroplasty to restore or improve cartilage health.
- Ligament reconstructions: Commonly performed for the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL).
- Loose bodies removal: This is where loose pieces of bone/cartilage are removed which are often fragments of cartilage from prior injuries.
- Diagnostic assessment: To assess the knee joint under direct vision using a camera.
During the procedure, the surgeon uses specialised instruments to treat the condition. The diagnosis is typically confirmed by thoroughly examining the joint with the arthroscope before proceeding with treatment.
How is Knee Arthroscopy Performed?
The procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The knee is cleaned, and anaesthesia is administered (commonly general anaesthesia).
- Arthroscope insertion: A small incision is made to insert the arthroscope, which transmits live images to a monitor.
- Diagnosis and treatment: Using specialised instruments, the surgeon diagnoses the issue and performs the necessary repairs or treatments, such as trimming/repairing torn meniscus, or repairing torn ligaments.
- Completion: The incisions are closed, and a bandage is applied.
Knee arthroscopy is often completed in less than an hour, depending on the complexity of the condition being treated.

What are the potential risks and complications?
Your surgeon takes every precaution to minimise risks of surgery, using state-of-the-art techniques and providing comprehensive preoperative and postoperative care.
Rest assured, your surgeon will carefully assess the risks and benefits before recommending surgery.
During your initial consultation, they will also discuss any specific risks relevant to your situation.
While knee arthroscopy is generally safe, some of the potential risks include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Nerve injury
- Stiffness or swelling
- Scarring
- Blood clots
- Pain
- Rare complications with anaesthesia
Our team prioritises safety and ensures every patient receives comprehensive care to minimise risks and promote optimal recovery.
What is the recovery time frames following surgery?
The arthroscopy procedure causes minimal tissue damage, depending on the extent of the intervention undertaken.
Most patients recover relatively quickly.
- Hospital stay: Patients typically are discharged the same day following surgery.
- Pain management: Medications and physical therapy help manage postoperative pain.
- Rehabilitation: Exercises to strengthen muscles and improve joint movement start shortly after surgery.
Time frames and post-op rehabilitation will depend on the exact treatment carried out during the surgery and should always be confirmed by your surgeon for individual cases.
As a general guide:
- 1–2 days after surgery
- You can eat and drink shortly after the procedure and should be able to walk, though crutches may be necessary for support.
- A brace may be provided dependent on the nature of the surgery carried out during the procedure e.g. meniscal repair patient often provided with knee brace.
- Avoid long walks or prolonged standing. When climbing stairs, lead with your good knee going up and your treated knee coming down.
- 3 days after surgery
- The surgeon will often recommend removing the wool and crepe bandage at 72 hours following the surgery, but to leave the ‘sticky wound dressings on’. This needs to remain in situ till wound inspection by a health care professional usually at 2 weeks. It is critically important to keep the wound dry during healing which can take up to 3 weeks and so protect it when having a shower. Before leaving the hospital, your healthcare team will provide detailed instructions on wound care.
- 1–2 Weeks after surgery
- Some patients may still observe pain and swelling and should still avoid overexerting themselves.
- Elevation of the knee using a pillow under the foot at nighttime, and application of ice can help reduce swelling more quickly.
- Physiotherapy exercises are important.
- 2 Weeks after surgery
- A wound check is advised by a healthcare professional to ensure all has healed as expected.
- The stitches from the keyhole sites if used are removed at this time.
- 6–12 Weeks After Surgery
- Most patients feel significantly recovered by six weeks, though some may need up to 12 weeks to feel fully normal.
- Recovery time varies depending on your condition and the procedures performed.
- Follow-up appointments with your surgeon at 6-8 weeks following surgery are important. During these visits: The surgeon will assess wound healing, knee movement, and determine the need for additional physiotherapy.
- Returning to Sports
- Avoid sports until the swelling subsides and your knee is strong enough to handle exercise.
- Your surgeon and physiotherapist will guide you on the appropriate timeline to resume sports safely dependent on the exact surgery carried out..
- Returning to work
- Before going back to work, consult your surgeon for personalised advice as it will depend on the treatment carried out within the knee.
- Returning to driving
- Refrain from driving until knee pain, swelling, and stiffness are resolved, and you regain full movement.
- You may be able to drive again approximately six weeks after your surgery, although this timeframe can vary between individuals. Your consultant will provide specific guidance based on your progress.
- Do not drive until you feel confident in controlling your vehicle and always confirm with both your doctor and your insurance provider before resuming driving.
What is the follow-up following surgery?
- A wound check and removal of stitches (if used) will be required at approximately 14 days after your surgery with a healthcare professional.
- A routine follow-up appointment with your surgeon will be needed around 6–8 weeks after your surgery.
How soon can you fly after knee arthroscopy surgery?
There is no specific formal medical guidance with respect to how long after surgery it might be before you are safe to fly.
Most surgeons and airlines recommend you should not fly within 6 weeks of surgery because of the increased risk of developing blood clots (Deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism).
Please check with your surgeon for any advice regarding air travel and any precautions to take if you have additional risk factors for blood clots.
What is the recommended rehabilitation? Tips for a smooth recovery
To strengthen your knee protect it from further injury, and support wound healing, follow these guidelines:
- Perform the exercises recommended by your physiotherapist 3 to 4 times daily for 6 weeks. Listen to your body and do not worry if cannot keep up as recommended.
- Elevation of the knee with a pillow under the foot (not under the knee) every nighttime over the first 4 weeks can help eventually reduce swelling more quickly.
- If you experience discomfort, take the prescribed painkillers until the pain subsides.
- It is critically important to keep the wound dry during healing which can take up to 3 weeks and so protect it when having a shower despite the dressing.
These steps will help ensure a safe and effective recovery.
How to maintain a healthy knee after surgery?
- Follow rehabilitation guidelines: Adhere to physiotherapy and exercise routines.
- Prevent falls: Use assistive devices and take precautions to avoid accidents.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet and healthy weight to reduce stress on the joint.
- Regular check-ups: Monitor the condition of the prosthesis through routine medical evaluations.
Summary: Why choose knee arthroscopy?
- A minimally invasive option for diagnosing and treating knee issues.
- Ideal for addressing injuries and conditions that impact daily life or athletic performance.
- Faster recovery and less discomfort compared to traditional surgery.
- Performed by a skilled surgeon using advanced technology for precise results.
Take the first step towards better knee health. Schedule a consultation today to explore how knee arthroscopy can help you achieve pain-free mobility and improved joint function.
