What is a knee replacement?
This is a procedure that involves replacing damaged parts of your knee joint with metal or plastic parts.
It is commonly used to alleviate pain and stiffness in the knee joint resulting from osteoarthritis.
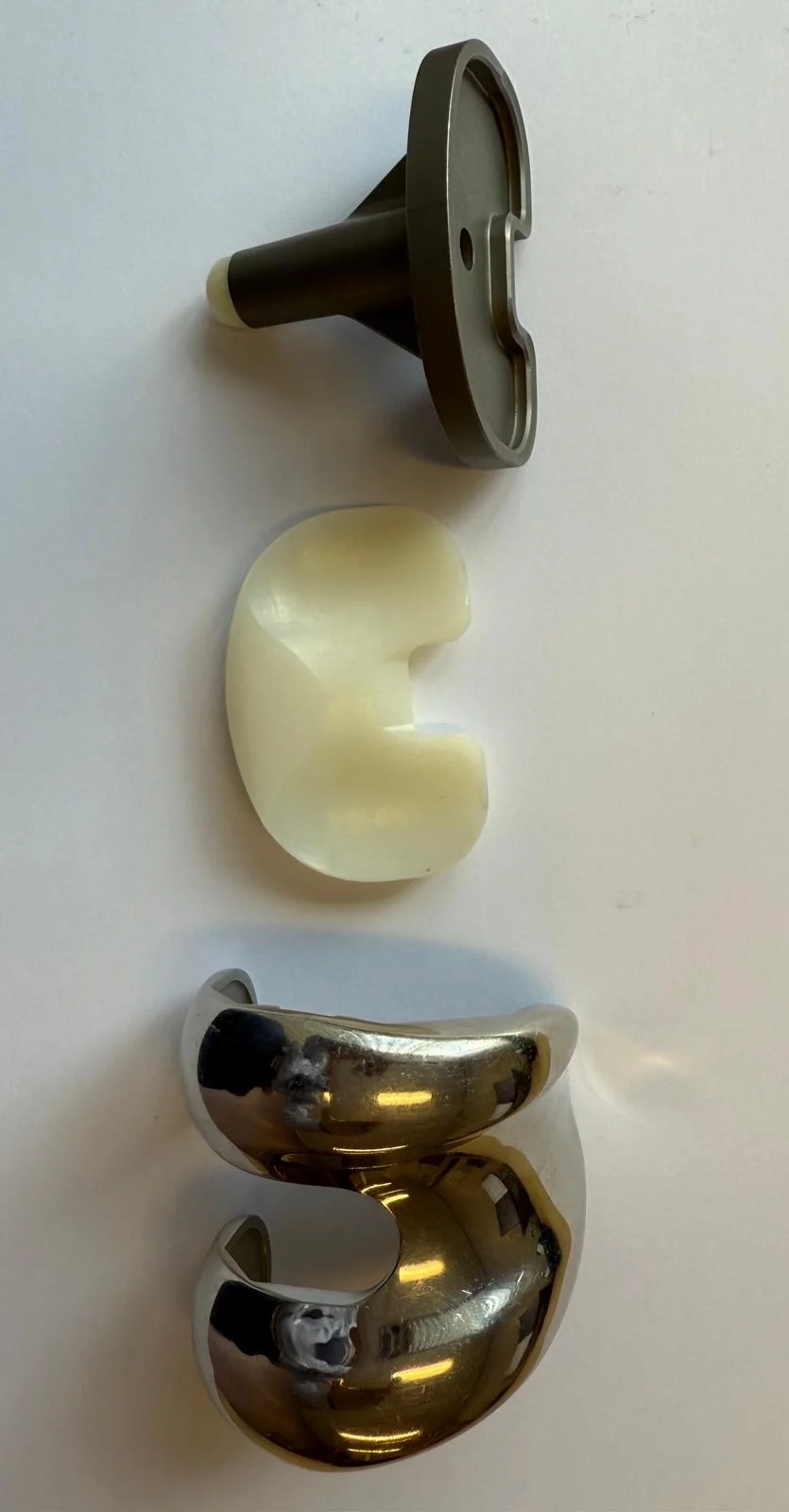

What are the types of knee replacement procedures?
- Total knee replacement: both sides of your knee replacement are replaced.
- Partial (unicompartmental) knee replacement: only one side of your knee affected is replaced
- Kneecap (patellofemoral) replacement: this involves replacing the under-surface of the kneecap and groove (trochlea) if these are the only parts affected by arthritis.
- Revision knee replacement: Replacement of a previously implanted knee prosthesis that has worn out or failed.
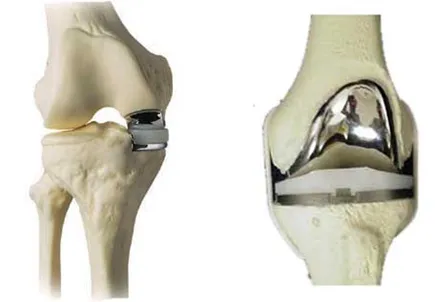
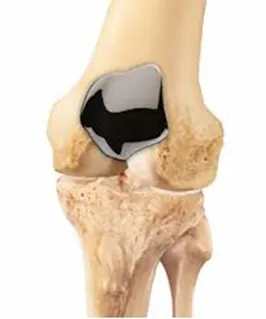
How does total knee replacement surgery allow mobility and comfort?
Knee replacement surgery is a transformative procedure designed to relieve pain, improve mobility, and enhance quality of life for individuals suffering from debilitating knee joint conditions.
Whether you’re an athlete aiming to get back to peak performance or someone struggling with everyday activities due to joint pain, advanced knee replacement techniques offer life-changing results. With a focus on precision and patient-centered care, your expert surgeon ensures high success rates and optimal recovery outcomes.
This advanced surgical option replaces a damaged or worn-out knee joint with a prosthetic implant, restoring function and comfort.
The knee typically moves smoothly because the ends of the bones are covered with a protective layer of tough tissue known as cartilage. When the cartilage is worn down or damaged, often due to injury, the bones begin to rub against each other, leading to pain and stiffness in the joint.
In a knee replacement, the damaged components of the knee are replaced with metal, and plastic parts.
Who can benefit from knee replacement?
Knee replacement is advised for individuals who:
- Experience chronic knee pain that limits daily activities, such as walking, getting dressed, and climbing stairs.
- Have tried other treatments, including medications, physiotherapy, and injections, without success.
- Suffer from severe joint damage due to osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or trauma.
- Seek to return to an active lifestyle, including sports or recreational activities.
If knee pain and stiffness are affecting your mobility and overall quality of life, a consultation can determine whether knee replacement surgery is the right solution for you.
It is most often used to relieve pain and stiffness in the knee joint caused by osteoarthritis.
Common causes of knee joint damage include:
- Osteoarthritis: Also known as “wear-and-tear arthritis,” where the protective cartilage cushioning the ends of bones within a knee joint wears away with time, causing the bones to rub against each other. This results in pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced mobility in the affected joint. It is the most common type of arthritis and frequently affects weight-bearing joints like the knees, hips, and spine.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the joint lining, resulting in pain and stiffness.
- Psoriatic arthritis: A form of arthritis that is linked to psoriasis- a chronic skin condition.
Other health conditions and issues that can damage your knee joint enough to require a knee replacement include:
- Fracture: Severe damage to the knee joint from a fall or similar accident may require replacement.
- Avascular necrosis: a painful bone condition that can deteriorate with time caused by reduced blood supply to one of your bones. A variety of risk factors for this include a traumatic event, sickle cell disease, steroid use, alcoholism, autoimmune disorders, and hypercoagulable states.
- Tumours: a group of abnormal cells that form lumps or growths which can start in any cells in the body and behave differently if they are cancerous (malignant) or benign (non-cancerous).
What are the other common causes of knee pain?
Knee pain is a frequent complaint that can affect individuals of all ages, from athletes to those with more sedentary lifestyles. It may result from injuries, medical conditions, or long-term wear and tear. Here are some of the other causes of knee pain:
- Meniscus tears: These are two crescent shaped tissues between the cartilage end of the knee joint, made of connective tissue. These act as shock absorbers to cushion both the cartilage ends of the knee joint.
- Damage to the knee cartilage (osteochondral defect): often caused by twisting or heavy lifting.
- Ligament injuries: Sprains or tears, such as ACL or MCL injuries, from sports or accidents.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of tendons due to repetitive strain or overuse.
- Bursitis: Swelling of the fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint.
- Patellofemoral pain syndrome: Pain around the kneecap from misalignment or overuse.
- Knee fractures: Breaks in the bones around the knee from trauma or osteoporosis.
What are the benefits of knee replacement surgery?
- Pain relief: Significant reduction or elimination of knee pain.
- Improved mobility: Greater range of motion and ability to perform daily activities.
- Enhanced quality of life: Increased independence and participation in recreational activities.
- Durable results: Modern implants often can last 15-20 years or more.
What are the alternatives to knee replacement surgery?
Most knee pain issues typically do not require surgery and can be managed with non-invasive treatments, including
- pain medication
- knee braces
- physiotherapy
- joint injections.
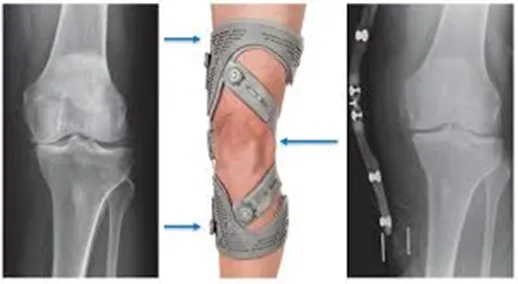
What happens during a knee replacement?
If you’re undergoing a knee replacement, you’ll typically be admitted to the hospital on the day of your surgery.
The procedure involves either a spinal anaesthetic, which numbs the body from the waist down while keeping you awake, or a general anaesthetic, which puts you to sleep throughout the operation.
If you opt for a spinal anaesthetic, you may also be given a sedative to help you stay calm and drowsy.
The surgery generally lasts around 1 to 2 hours, and the specific approach taken will depend on factors such as the extent of knee damage, its underlying cause, and your overall health.
Our surgeon uses advanced techniques to ensure a smooth and successful procedure. Here’s what to expect:
- Preparation: The area is carefully sterilised, and anaesthesia is administered for comfort.
- Surgery: The surgeon removes damaged cartilage and bone from the knee joint and replaces them with custom-fitted prosthetics. These components are secured for stability and natural movement.
- Precision tools: Image-guided technology and minimally invasive methods are often utilised to enhance accuracy and reduce recovery time.
- Completion: The joint is tested for proper alignment and mobility before closing the incision.
What does the recovery and rehabilitation involve?
- Hospital stay: Patients typically stay in the hospital for 0-3 days.
- Pain management: Medications and physical therapy help manage postoperative pain.
- Rehabilitation: Exercises to strengthen muscles and improve joint movement start shortly after surgery.
- Return to activity: Most individuals resume normal activities within 12 weeks, with improvements continuing over several months. Improvement in pain have been shown to occur up to 1- 1.5 years following the surgery.
What are the potential risks and complications?
Your surgeon takes every precaution to minimise risks of surgery, using state-of-the-art techniques and providing comprehensive preoperative and postoperative care.
Rest assured, your surgeon will carefully assess the risks and benefits before recommending surgery.
During your initial consultation, they will also discuss any specific risks relevant to your situation.
While knee replacement is a widely successful procedure, risks are rare but possible and some of these can include:
- Infection.
- Nerve or blood vessel damage
- Blood clots.
- Implant wear or loosening over time.
- Dislocation of the prosthetic joint.
- Ligament injury
- Joint stiffness
- Bone fracture
- Anaesthetic risk
What is the recovery like at home? Tips for a smooth recovery
When you return home, you may feel quite tired. Prioritise rest initially, then gradually increase your activity levels to aid recovery.
To strengthen your knee protect it from further injury, and support wound healing, follow these guidelines:
- Perform the exercises recommended by your physiotherapist 3 to 4 times daily for 6 weeks. Listen to your body and do not worry if cannot keep up as recommended.
- Engage in low-impact activities like walking and gradually increase the distance as you feel comfortable. The balance between strengthening exercises versus walking distance should favour strengthening exercises initially, as this will allow you to achieve an increased walking distance.
- Elevation of the knee with a pillow under the foot (not under the knee) every night time over the first 6 weeks can help eventually reduce swelling more quickly.
- Sitting in a chair ensuring the knee is bent to at least 90 degrees from day 1 post-operatively and onwards on some occasions EVERY day can really help in ensuring a good range of knee motion is finally achieved.
- Refrain from lifting heavy objects or engaging in strenuous activities.
- Continue using crutches or a walking stick for support as long as needed.
- If you experience discomfort, take the prescribed painkillers until the pain subsides.
- It is critically important to keep the wound dry during healing which can take up to 3 weeks and so protect it when having a shower despite the dressing.
These steps will help ensure a safe and effective recovery.
How to maintain a healthy knee after surgery?
- Follow rehabilitation guidelines: Adhere to physiotherapy and exercise routines. You need to really work on your range of motion exercises, because you have up to 3 months post-operatively to achieve your maximum potential in most cases
- Prevent falls: Use assistive devices and take precautions to avoid accidents.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet and healthy weight to reduce stress on the joint.
- Regular check-ups: Monitor the condition of the prosthesis through routine medical evaluations.
When can I drive a car after surgery?
You may be able to drive again approximately six weeks after your surgery, although this timeframe can vary between individuals. Your surgeon will provide specific guidance on when you’re ready. Do not drive until you feel confident in controlling your vehicle and always confirm with both your doctor and your insurance provider before resuming driving.
When can I return to work after surgery?
Before going back to work, consult your surgeon for personalised advice. As a general guideline:
- Sedentary jobs (e.g. office-based work): You can typically return after 4–6 weeks.
- Mixed-labour jobs (e.g. teacher): You may return after about 3 months.
- Manual labour jobs (e.g. builder): You should wait approximately 6 months before resuming work.
How soon can you fly after hip replacement surgery?
Most surgeons and airlines recommend you should not fly within 3 months of surgery because of the increased risk of developing blood clots (Deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism).
Please check with your surgeon for any advice regarding air travel and any precautions to take if you have additional risk factors for blood clots.
What is the follow-up schedule after surgery?
A wound check will be required at approximately 14 days after your surgery with a healthcare professional.
A routine follow-up appointment with your surgeon will be needed around 6–8 weeks after your surgery.
Summary: Key Points to Remember
- Knee replacement surgery restores mobility and relieves pain for those with severe knee joint damage.
- It’s an excellent option for individuals whose daily activities or sports performance are impacted by knee issues.
- Advanced surgical methods ensure precise results and faster recovery.
- A robust aftercare plan, including physiotherapy, is essential for optimal outcomes.
Don’t let knee pain hold you back. Schedule a consultation today to learn how our expertise in knee replacement surgery can help you regain your active lifestyle.
